Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder
What is Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder?
Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder, also commonly known as ADHD, is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that can be found in children, teens, and adults. It is with ADHD that one’s behavior is impacted in a manner in which one finds themselves experiencing trouble concentrating, acting impulsively, and feeling restless. Listed below is an informational video created by Psych Hub that provides a more in-depth explanation as to what ADHD entails:
What Does ADHD Look Like?
Here is a video by Olivia Lutfallah that simulates what ADHD might look like for a person who is affected by it:
What Causes ADHD?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) the causes and risk factors for ADHD are currently unknown. However, current research by scientists suggests that genetics may play an important role in what could be causing one to have ADHD. In addition to this scientists are also researching other possible causes of ADHD, such as:
- Brain injury
- Exposure to environmental risks during pregnancy or at a young age
- Alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy
- Premature delivery
- Low birth weight
How is ADHD Diagnosed?

ADHD is one the most commonly diagnosed neurodevelopmental disorders, but the process behind diagnosing one with ADHD is a process in which several steps are taken. Although ADHD is a commonly diagnosed disorder there is no single test to diagnose it as the symptoms of the disorder are similar to those of other disorders, such as:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Sleep Problems
- Other learning differences
According to the CDC one step involved in the process of diagnosing ADHD is conducting a medical exam, which includes both hearing and vision tests in order to help rule out other disorders with symptoms similar to ADHD. Additionally, healthcare providers will also use the guidelines in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) to help in the process of diagnosing ADHD. According to the DSM-5 criteria for ADHD, it states that “People with ADHD show a persistent pattern of inattention and/ or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development.” It is based on this criteria along with other conditions, such as:
- Several inattentive or hyperactive-impulsive symptoms were present before the age of twelve
- Several symptoms are present in two or more settings
- There is clear evidence that the symptoms interfere with social, school, or work functioning
- They symptoms are not explained by another mental disorder
Now, unfortunately ADHD is not something that ever really goes away with age, but it can become easier to deal with as you go into adulthood. According to the CDC, to diagnose ADHD in adults or those aged 17 or older, only five symptoms are necessary as opposed to the six necessary to diagnose children. However, diagnosing ADHD in adults can become a bit of a challenge as symptoms may look different compared to those in children.
What are the Statistics?
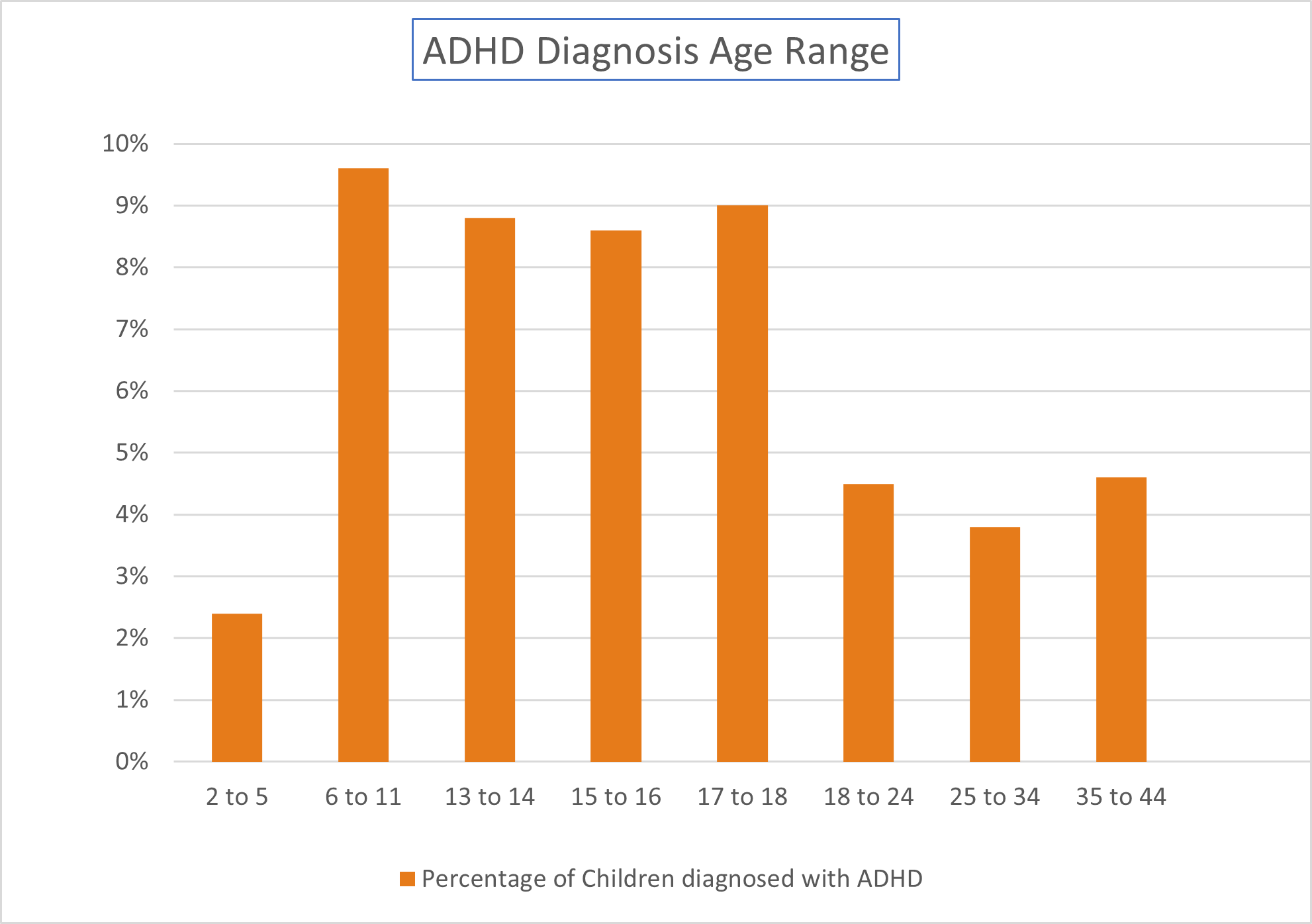
When it comes to the ADHD statistics in children it has been found that “The percentage of children ever diagnosed with ADHD increases with age.” According to the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry about 2.4% of children who are between the ages of 2 and 5 years old have been found to be diagnosed with ADHD. Along with 9.6% of children between the ages of 6 and 11 years old as well as shown in the graph above.
In addition to this, about 8.8% of teens between the ages of 13 to 14 years old have been diagnosed with ADHD. Additionally, it has been found that 8.6% of teens between the ages of 15 and 16 years old are diagnosed with ADHD. Finally, about 9% of teens between the ages of 17 and 18 years old are found to be diagnosed with ADHD.
Finally, about 4.5% of adults between the ages of 18 and 24 years old are found to have been diagnosed with ADHD. Whereas 3.8% of adults between the ages of 25 to 34 years old have the diagnosis. Lastly, 4.6% adults between the ages of 35 to 44 years old are found to be diagnosed with ADHD.
What are the Different Types of ADHD?

Now that we have an understanding as to the general definition of ADHD along with the possible causes behind it and the diagnosis process we can begin to discuss the different types of ADHD. There are three different types of ADHD:
- Inattentive ADHD
- Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD
- Combined ADHD
What is Inattentive ADHD?
Inattentive ADHD, which was once known as ADD, is a type of ADHD disorder in which one often finds themselves experiencing a limited attention span, distractibility, and forgetfulness. It is with this type of ADHD disorder that people oftentimes have difficulty finishing or focusing on tasks at work or school, along with the ability to organize as well. Those with inattentive ADHD also find themselves easily distracted by external stimuli.
Symptoms of Inattentive ADHD:
- Making careless mistakes
- Limited attention span
- Poor listening skills
- Difficulty completing tasks
- Disorganization
- Avoidant behavior
- Distractibility
What is Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD?
Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD is the least common type of ADHD disorder that is often characterized by the need for constant movement. Although it is the least common type of ADHD disorder it is the easiest to diagnose as it is the most recognizable one of the three types. Those who are affected by hyperactive-impulsive ADHD often struggle staying still and with self-control. (Add footnote to additudemag types of adhd website)
Symptoms of Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD:
- Restlessness
- Difficulty staying still
- Difficulty engaging in activities
- Impatient
- Acting out of turn
- Talking constantly
What is Combined ADHD?
Combined ADHD, like the name states, is a combination of both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive ADHD. When one is affected by combined ADHD their symptoms do not exclusively fall within inattentive or hyperactive-impulsive ADHD, but rather they experience a combination of symptoms from both types. However, symptoms may change overtime as you get older meaning that the type of ADHD that you may have can change.
What are Some Ways to Combat ADHD?
Now, as college students you find yourselves experiencing busy schedules filled with homework assignments and projects and it becomes difficult to deal with these things including balancing your school life and personal life when having ADHD. As a college student ADHD can affect you academic performance, time management, and your ability to regulate your emotions. Here are seven tips by Keath Low from Very Well Mind that could help you succeed in college when you have ADHD: (Add footnote to verywell mind website)
- Start the Day on Time
- If getting out of bed in the morning is the problem make sure to set a few alarms to go off in the morning. Putting your alarm across your room away from your bed will help motivate you to get out of bed as well.
- If getting sidetracked in the morning is the problem, figure out how much time you need to get ready in the morning and set alarms for when you should get dressed, when you should eat, and so on.
- Work with your urge to procrastinate
- If you feel the urge to procrastinate when working on your assignments then go with that feeling because sometimes the only time to get things done when you have ADHD is before it's due. Now, this might sound counterproductive, but as an example to help you understand better let’s say you have a paper to write. Make sure that you have done the reading and/or research and have the information that you need to write it. In addition to this, figure out how long it might take you to write the paper and schedule it with the deadline in mind that way even if you procrastinate you know you can get it done.
- Study smarter, not harder
- Studies show that multimodal learning helps those learn better so rather than trying to force yourself to memorize the information try to get creative with it by:
- Highlighting text in different colors
- Record voice notes to listen to later
- Try reading aloud to yourself
- Work with a friend or classmate
- Studies show that multimodal learning helps those learn better so rather than trying to force yourself to memorize the information try to get creative with it by:
- Schedule your study time
- Plan your time: Assess and prioritize
- Stick to your plan
- Manage your medication
- Make sure to stay on top of your medications that you need in order to help with your ADHD. If you have trouble remembering to take your medication you can set an alarm for yourself everyday to remind you.
In addition to the seven tips listed above for college students with ADHD here is a video by Psych Hub in which Ned Hallowell, an MD, psychiatrist, and world authority on ADHD, discusses five tips for living with ADHD: