Week 2: Framing & Camera Basics
To Do By Class
Install the free Blackmagic Camera app (iOS/Android) for manual control.OPTIONAL! (not everyone has access to this app- Watch the Master Blackmagic iPhone Camera App - FULL Guide tutorial” Its kind of long, but it will give you a good way to navigate the app.
- Watch the Ultimate Guide to Film Composition & Framing — Key Elements Explained. This will help orient you to key terms.
- Journal (hand-written on paper) about a favorite movie or short. Look at ONE SCENE/SEQUENCE of this movie online. Try to describe the framing techniques.
*In class I will randomly call on people about their journal entries! (10% particiaption grade)
Module Notes
*NOTE: Class critiques and learning....In-class Framing Assignment
- 5 Shot Short Film
- DTC208-Phone-Thief-Group-Exercise-1
- DTC 208 5 shot mini film edit
- (Prather, Joshua) Five Shot Mini-Assignment
- DTC 208 Mini-Assignment 1
- The late student
- 5 Shot Silent Short Film
- Logan Keller - 5 Shot Silent Film
Smartphone Camera Fundamentals
- Resolution & Frame‑Rate: 720p or 1080p @ 30fps or 24fps
- Focus: tap‑hold to lock; use AF only for rack‑focus practice or when moving with camera.
- Allow 10 secs of recording before and after "action"
- Hold camera steady on shot
- Move in closer rather that using Zoom
- Shoot horizontal or landscape mode.
- Pay attention to lighting on subject
Tools Overview
- Using the Blackmagic Camera app
- Using a monopod, tripod, small tripod grip
- Static and Moving Camera
Classical Hollywood Three-Point Lighting
- Key Light: primary source; place at 45° to subject; strongest light.
- Fill Light: opposite key; softens shadows; use dimmer or bounce.
- Back Light (Rim/Hair): behind subject; separates from background; adds depth.
- Budget Tip: use LED panels, clamp lights, or window light with DIY modifiers.
- DIY Diffusion: try wax paper, shower curtain, or white bedsheet.
Lens Lengths and Depth of Field
- Zoom/Telephoto: Creates a shallow depth of field, isolating subject from background.


- Wide Angle: Enhances deep focus, keeping more of the scene sharp.
Composition
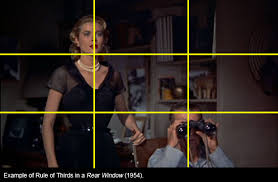
- Rule of Thirds: Divides frame into thirds, placing subjects on intersections for balance and interest.

Shot Types
-
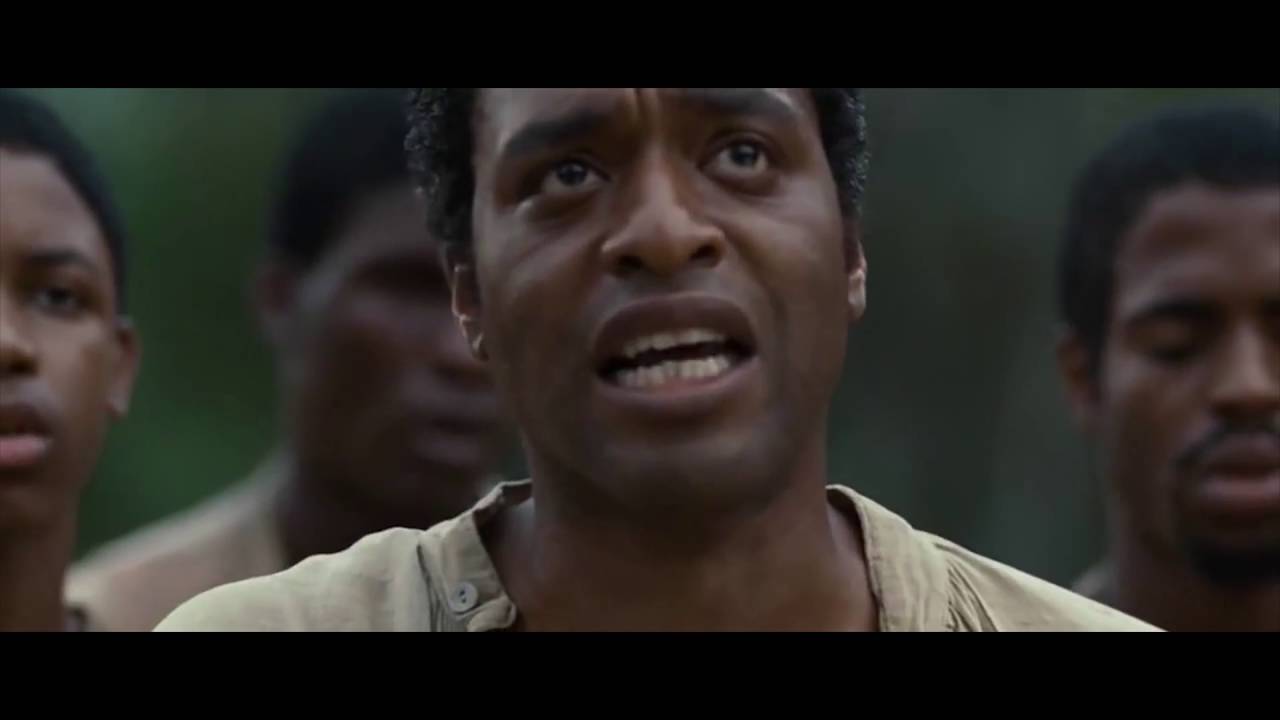
Close-Up (CU): Frames the subject’s face; emphasizes emotion and detail.

-
Medium Shot (MS): Frames subject from waist up; balances subject and environment.

-
Long Shot (LS): Shows entire subject and some background; establishes context.
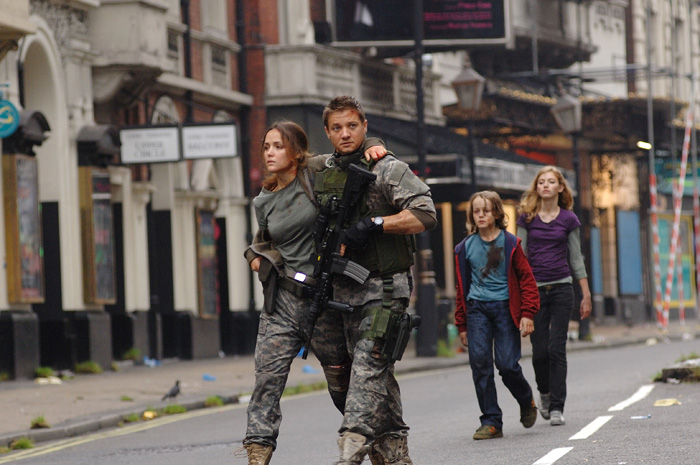

-
Medium Close-Up (MCU): Frames subject from chest or shoulders up.
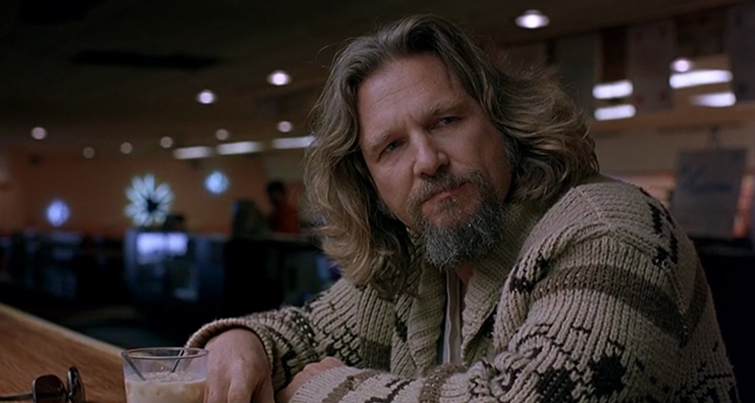

-
Medium Long-Shot (MLS): Frames subject from knees up; balances subject and environment.

-
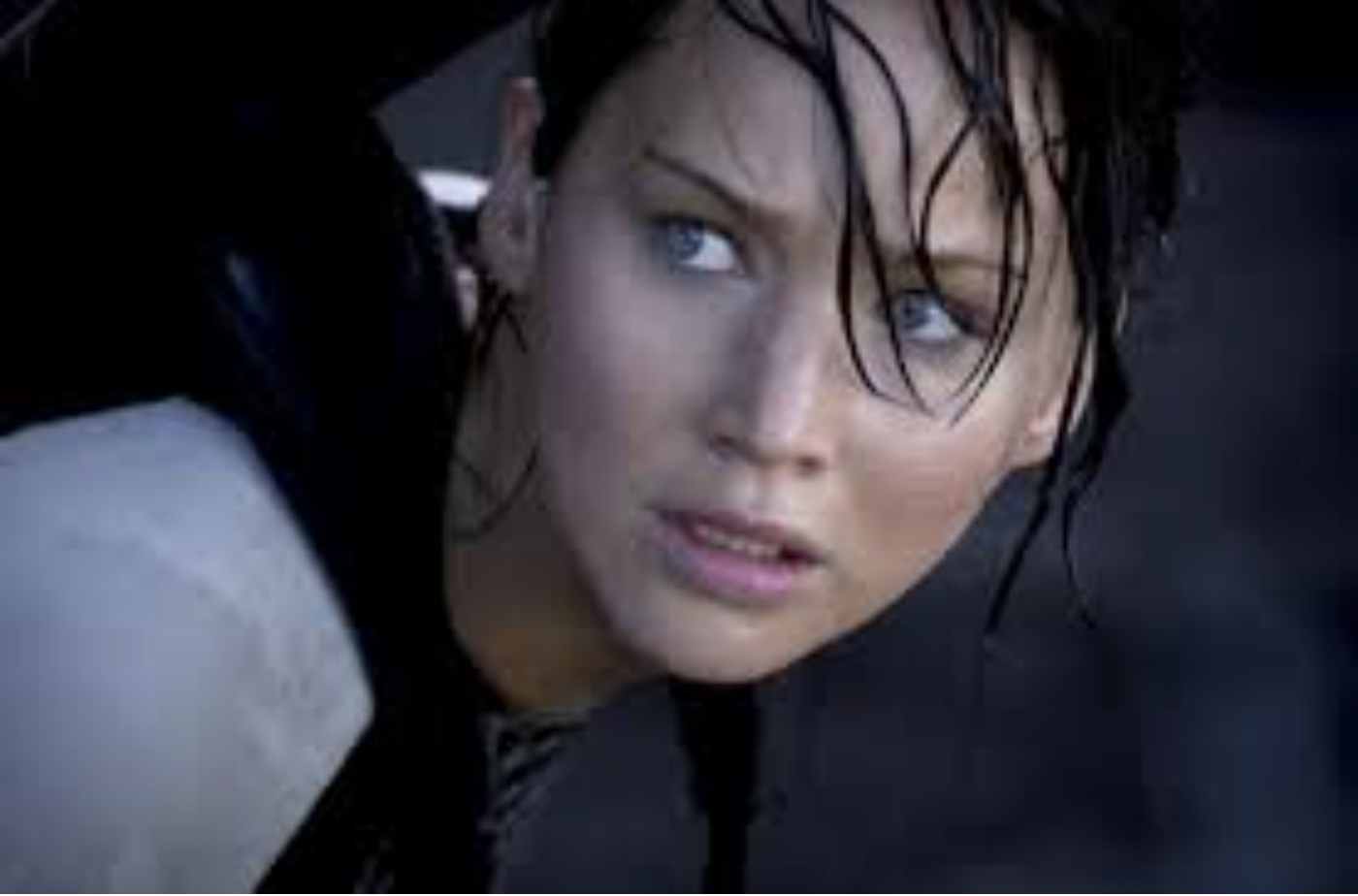
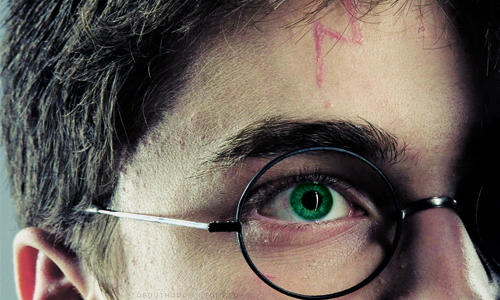
Extreme Close-Up (ECU): Focuses on a detail (eye, hand); intensifies drama.
-
Extreme Long Shot (ELS): Emphasizes scale or environment; often an establishing shot.

Framing Types
-
Over-the-Shoulder (OTS): Shows perspective from behind a character’s shoulder; common in dialogues.

-
Point-of-View (POV): Simulates what a character sees; increases immersion.


-
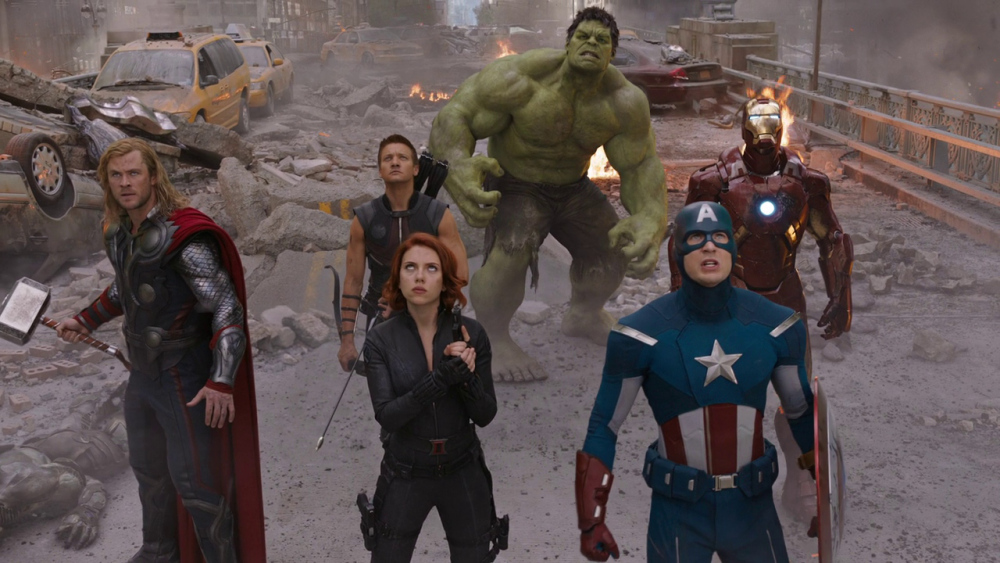
Two-Shot: Frames two characters; used in interactions and comparisons.

-
High Angle: Camera looks down on subject; suggests vulnerability or powerlessness.

-
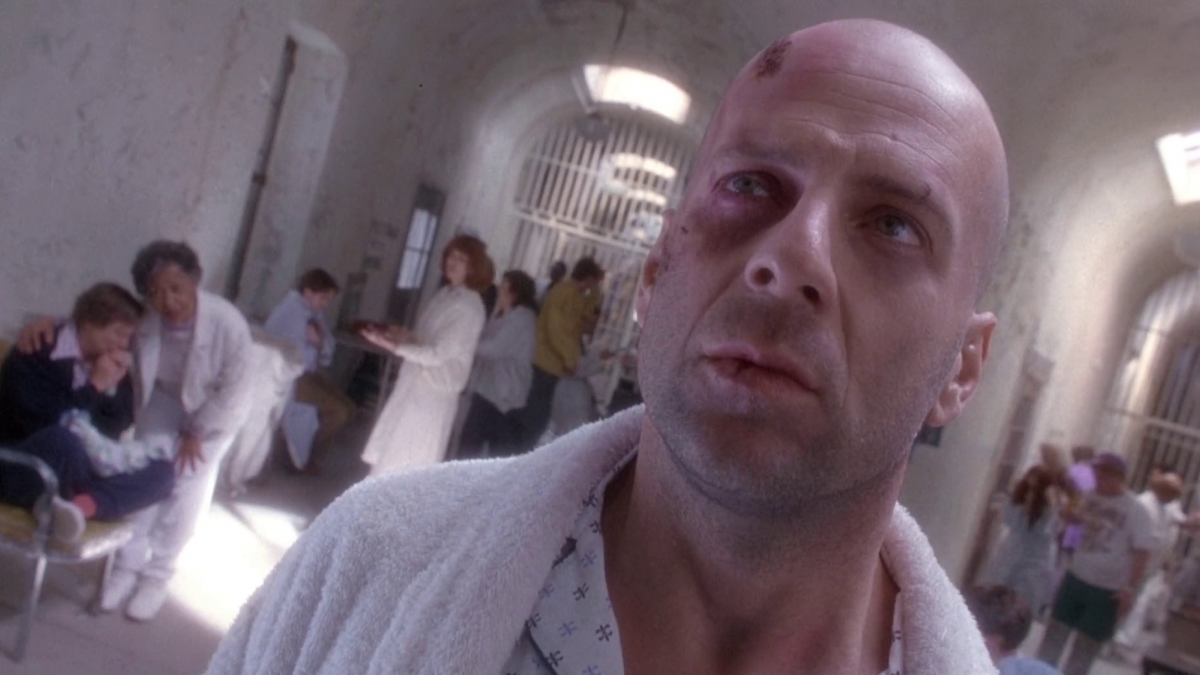
Low Angle: Camera looks up at subject; implies dominance or strength.

-
Dutch/Canted Angle: Camera rotated left or right; implies something is off.

Camera Movements
-
Tilt: Moves the camera up or down on its vertical axis; simulates looking up or down.
-
Pan: Moves the camera left or right on its horizontal axis; follows action or reveals space.
-
Track / Dolly: Moves the entire camera smoothly forward, backward, or sideways, often on tracks or wheels.
-
Crane: Moves the camera up or down through space using a crane or jib; often dramatic and sweeping.
-
Zoom: Changes focal length to move closer or farther from subject without moving the camera.
-
Handheld: Camera is held by the operator, producing a shaky, immediate, and intimate feel.
-
Steadicam / Gimbal: Stabilized camera movement that follows subjects smoothly without visible shake.
-
Push-In / Pull-Out: Moves the camera smoothly closer to (push-in) or away from (pull-out) the subject to emphasize emotion or reveal context.
-
Whip Pan: A fast pan that creates a blur, often used for transitions or to convey speed.
-
Rack Focus (Focus Pull): Shifts the focus from one subject to another within a shot, guiding viewer attention.
Framing Examples
Framing Assignment (5%)
DUE Sept 5th – Submit YouTube/Vimeo URL to Canvas AND post the link to Slack before class.
Objective: Tell a short 20–30 second story using 5 well-composed shots to create a visual narrative. This assignment focuses on framing and camera position—no dialogue and no camera movement.
Guidelines:
- Use only 5 shots (each carefully framed).
- No camera movement (panning, tilting, zooming).
- No music track or voice-over. Natural sound and simple sound effects are allowed.
- Each shot should clearly connect to the next, establishing spatial and narrative relationships.
Examples of story ideas:
- The aftermath of a guilty pet making a mess in the kitchen.
- Someone looking around the house for an annoying sound.
- Someone anxious about opening a letter they just picked up from the mailbox.
Tips for visual storytelling:
- Think about how professional films start: often with a wide shot of the setting, then medium shots of the characters, and close-ups for details (faces, objects, hands).
- You can also reverse this order—begin with a close-up, then slowly reveal the context.
- The grammar of visual storytelling lies in these shot-to-shot connections:
• A wide shot of a person, followed by a close-up of their eyes, creates a spatial whole.
• Each frame defines relationships in space and time.
Goal: Show how framing choices alone (without camera movement or dialogue) can shape meaning and emotion in a story.
Continuity Editing
- Continuity System – spatial, temporal, and causal coherence
- 180° Rule – maintaining consistent screen direction
- 30° Rule – camera movement threshold between cuts
- Eyeline Match & Point-of-View
- Match on Action – cut hides the edit with continuous movement
- Cutaway & Insert shots for pacing / hiding jump cuts