Multimedia fiction combines key aspects of hypertext fiction, kinetic and interactive poetry, and interactive fiction to combine digital writing into immersive pieces of art. Combining sound, animation, storytelling, interactivity, and more to captivate the reader, multimedia fiction paints a fictional space for its audience. Much like the previously mentioned forms of electronic literature, multimedia fiction is a museum for fanatics of the avant-garde, but it also contains simpler pieces for those who prefer straightforward art.
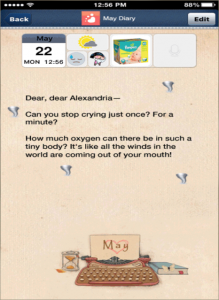
A simpler example of multimedia fiction is Alan Bigelow’s “How to Rob a Bank – Part 4”, which follows the daily diary of a new mother trying to raise her baby as she realizes she and her husband are growing apart. By using outside environment sounds and the interface of a phone to emulate a person using their phone outside to write up diary entries, the protagonist becomes much more human. By documenting the decline of the mother’s mental state as she becomes more stressed from motherhood and her relationship with her husband within this outline of a phone, the piece is presented as a fictional but immersive story.
A more abstract piece of multimedia fiction is Mark Amerika’s “FilmText”, which puts the reader in a simulated environment, akin to a video game. The reader can click on various cones being emitted from craters to open up different documents that explain the universe of the piece. “FilmText” stands out much more as a piece of fiction with its sci-fi elements arising from Amerika’s creation of ideas like a “Digital Thoughtographer”, but it still manages to be immersive like “How to Rob a Bank – Part 4”.

Multimedia fiction manifests itself in many different forms to allow for its writers to convey their message in any way they choose. Whether it is immersive, simple, abstract, or more, multimedia fiction appeals to fans of writing, technology, avant-garde, and the like.