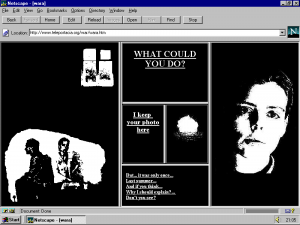
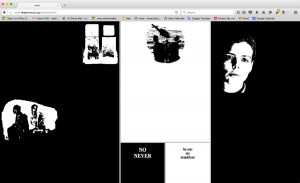
In reading World of Awe, the way it is presented made me think of the old CD-ROM games I used to play as a kid. Following the journey of “the traveler” the reader is bounced from first-person accounts to letters he has written to a lover. Also one gets the sense that technology is very precious in this fictional world, as the traveler seeks out any piece he can find, in this virtual desert.
I did find it extremely helpful to read the “about world of awe” piece, because there were some parts of the reading I was unsure of, and it was able to clarify certain plot points. Like the fact that the letters on the computer were unsent, to the traveler’s unknown lover. In the first chapter, he speaks about this person with great yearning, saying how he carries around a piece of cloth of their’s just for comfort.
The intertextuality between this piece and Uncle Buddy’s Phantom Funhouse is what caught me. They both are fragmented looks at a person’s life. Although personally, I preferred World of Awe to Funhouse. The story is easier to follow, and maybe it’s the 90’s kid in me but I liked the format, it definitely felt familiar and nostalgic.
This is not a story that has much variability unless one chooses to read the chapters out of order. Which with most of the readings so far that has been the case.
The artwork I think is a key part of telling the story, it adds another layer of understanding with these visual references.
Overall, I really enjoyed this piece.